Importing Content with the API
Before you Begin
The following information is applicable to our original import format (called version 1 imports) in order to support new features and increased flexibility Carbon editor supports a new expanded import format (version 2 imports). If you are implementing imports for the first time or as a proof of concept you may wish to continue using version 1 imports for their simplicity, however we recommend that you transition to version 2 imports for production workflows as all new feature development and support will be on version 2 imports. For details on version 2 imports see Version 2 Imports
Please take note of this important information:
- Updating existing Pages using the Import API will be available in an upcoming release. For now, importing content will result in new Pages being created in the selected Document.
- The imported content can be:
- A sole XML file representing one Page, or
- A .zip file containing one XML file for each Page to be created in Carbon Editor.
- XML documents define the field types using the "field_type" attribute.
- XML documents must be saved with UTF-8 as encoding. Otherwise, content might not import correctly.
- Please ensure your XML is valid against the Liquid State Carbon Editor XSD.
- For more information, see Carbon Editor XML Format.
- You can use online tools such as this one to perform ad-hoc checks.
Creating a new Document with the API
Before creating your document, please ensure your content is prepared in a recognisable format.
To create a new Document using the API, you will need your API Token, and the endpoint API URL of the Space.
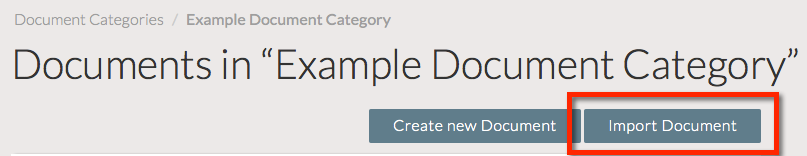
To retrieve these details, navigate to the Document Category in which you want to create the new Document.
Click the Import Document button.
Your API Token and the endpoint API URL associated with the Space are listed within the Content API section.
To begin your import, make a POST request to the endpoint using the parameters below:
| POST Request Headers | |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| Authorization | Token API_TOKEN |
| POST Request Parameters | |
| name | Name of the new Document |
| POST Response Details | |
|---|---|
| Content Type | application/json |
| POST Response Content | |
| UUID | Unique identifier for the newly created Document. This is a UUID version 4 identifier. |
| URL | The API URL to access this document. |
| Name | The name of this document |
| Slug | The slug used to identify this document in the Carbon Editor interface |
| Imports | The API URL used to access the list imports for this document |
Importing pages with the API
Using the API, you can import pages in to an existing Document.
You can add pages to a document using the API, regardless of whether the document was originally created with Carbon Editor, or via the API.
You will need your API Token and the endpoint API URL of the specific document you are adding new pages to.
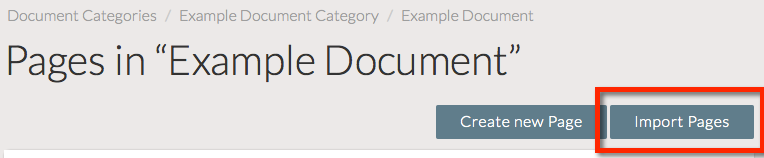
To retrieve your API Token and the endpoint API URL, navigate to the relevant Document.
Click the Import Pages button.
Your API Token and the endpoint API URL associated with the document are listed within the Content API section.
To begin your import, make a POST request to the endpoint using the parameters below:
| POST Request Headers | |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | multipart/form-data |
| Authorization | Token API_TOKEN |
| POST Request Parameters | |
| import_file | The .xml or .zip file containing the page or pages you wish to import. |
| POST Response Details | |
|---|---|
| Content Type | application/json |
| POST Response Content | |
| UUID | Unique identifier for the newly created Document. This is a UUID version 4 identifier. |
| URL | The API URL you can access to get details on this import |
| Status | The current status of the import, progresses from started to complete. Statuses:
|
| failure_message | If something is wrong with your import, more details will be provided in this field |
| total_pages | Once the import has started, this will reflect the total number of pages to be created. |
| created_pages | This is the current number of pages which have been created. |
| modified_at | The datetime when this import was last updated. |
Example Python 3 Script: Create a New Document, Import a Page in to Document
# use the python-requests library: http://docs.python-requests.org
import requests
IMPORT_FILE = './page.xml'
API_TOKEN = 'XXXXXXXXXXX'
ENDPOINT_URL = 'https://editor.liquid-state.com/api/v1/organisations/XXXXXX-ed4c-4e11-976c-06c348af546d/spaces/XXXXXXX-bw58-4484-8e88-60d305ca9e15/documents/'
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Token {}'.format(API_TOKEN)
}
data = {
'name': 'My new Document'
}
response = requests.post(ENDPOINT_URL, data=data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
response_obj = response.json()
new_doc_uuid = response_obj['uuid']
doc_url = response_obj['url']
imports_url = response_obj['imports']
print(new_doc_uuid)
files = {'import_file': open(IMPORT_FILE, 'rb')}
response = requests.post(imports_url, files=files, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
print('done')
else:
print("Couldn't upload file")
else:
print("Couldn't create document")
Your API token is a unique identifier for your user account.
Permissions applied during an API call reflect the permissions associated to the user the API token belongs to.
Related content
Unless otherwise indicated in the Overview page of this WIKI the information contained within this space is Classified according to the /wiki/spaces/ISMS/pages/739344530 as |
INTERNAL |